101 Essentials Cybersecurity Tools and Frameworks for 2025
101 Essentials Cybersecurity Tools and Frameworks for 2025
Introduction
In today’s digital age, cybersecurity is a top priority for businesses and individuals alike. With the increasing number of cyber threats and attacks, it’s essential to have the right tools and frameworks in place to protect your digital assets. In this article, we’ll explore the 101 essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks that you need to know in 2025.
The objectives of this article are to:
- Provide an overview of the importance of cybersecurity in 2025
- Identify the essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks for businesses and individuals
- Discuss the potential benefits and drawbacks of implementing these tools and frameworks
- Offer suggestions and professional pieces of advice for improving cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is crucial for protecting digital assets from cyber threats and attacks. A single breach can result in significant financial losses, reputational damage, and compromised sensitive data. In 2025, cybersecurity is no longer a luxury but a necessity for businesses and individuals alike.
The purpose of this article is to provide a comprehensive guide to the 101 essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks for 2025. This article aims to educate readers on the importance of cybersecurity and provide them with the knowledge and tools needed to protect their digital assets.
Overview:
Overview of Profitable Earnings: Investing in cybersecurity can have a significant return on investment (ROI). According to a recent study, the global cybersecurity market is expected to reach $300 billion by 2025. By implementing the right cybersecurity tools and frameworks, businesses can protect their digital assets, reduce the risk of cyber attacks, and improve their bottom line.
The potential benefits of implementing cybersecurity tools and frameworks are numerous. Some of the potential benefits include:
- Improved security posture
- Reduced risk of cyber attacks
- Increased customer trust and confidence
- Improved compliance with regulatory requirements
- Increased ROI
101 Essentials Cybersecurity Tools and Frameworks for 2025
Here are 101 essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks for 2025:
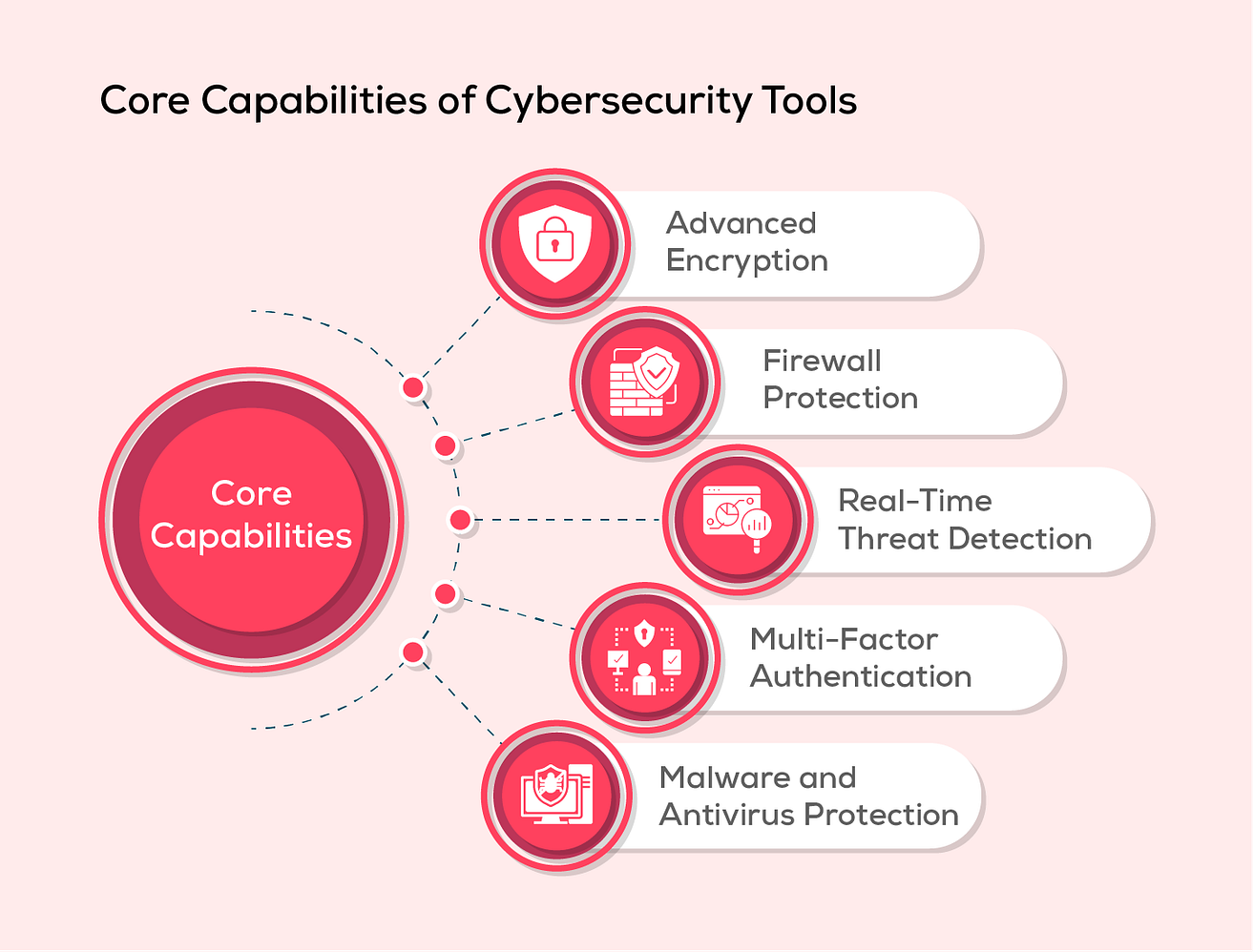
1. Firewalls: Network security systems that control incoming and outgoing network traffic.
2. Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Systems that detect and alert on potential security threats.
3. Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS): Systems that detect and prevent potential security threats.
4. Encryption: Technology that protects data by converting it into an unreadable format.
5. Incident Response Plans: Plans that outline procedures for responding to security incidents.
6. Antivirus Software: Software that detects and removes malware.
7. Virtual Private Networks (VPNs): Networks that provide secure, encrypted connections.
8. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Authentication methods that require multiple forms of verification.
9. Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) Systems: Systems that monitor and analyze security-related data.
10. Penetration Testing: Simulated cyber attacks on an organization’s computer systems.
11. Vulnerability Assessment: Identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities in an organization’s systems.
12. Compliance Frameworks: Frameworks that outline requirements for regulatory compliance.
13. Cloud Security: Security measures designed to protect cloud-based data and systems.
14. Endpoint Security: Security measures designed to protect endpoint devices.
15. Network Segmentation: Dividing a network into smaller, more secure segments.
16. Identity and Access Management (IAM): Systems that manage user identities and access.
17. Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Systems that detect and prevent data breaches.
18. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response (SOAR): Systems that automate security incident response.
19. Threat Intelligence: Information about potential security threats.
20. Cybersecurity Governance: Frameworks that outline roles and responsibilities for cybersecurity.
21. Risk Management Frameworks: Frameworks that outline processes for managing risk.
22. Security Awareness Training: Training programs that educate users about security best practices.
23. Incident Response Teams: Teams that respond to security incidents.
24. Digital Forensics: The process of collecting and analyzing digital evidence.
25. Cybersecurity Consulting: Consulting services that help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture.
26. Managed Security Services: Services that provide ongoing security monitoring and management.
27. Security Testing: Testing that simulates cyber attacks to identify vulnerabilities.
28. Compliance Monitoring: Monitoring that ensures adherence to regulatory requirements.
29. Security Architecture: Designing and implementing secure systems and architectures.
30. Cloud Workload Protection: Security measures designed to protect cloud-based workloads.
31. Container Security: Security measures designed to protect containerized applications.
32. DevOps Security: Integrating security into DevOps practices.
33. Application Security: Security measures designed to protect applications.
34. Network Security: Security measures designed to protect networks.
35. Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR): Systems that detect and respond to endpoint threats.
36. Security Analytics: Analyzing security-related data to identify potential threats.
37. Threat Hunting: Proactively searching for potential security threats.
38. Incident Response Planning: Planning for potential security incidents.
39. Disaster Recovery: Planning for business continuity in the event of a disaster.
40. Business Continuity Planning: Planning for business continuity in the event of a disaster.
41. Cybersecurity Frameworks: Frameworks that outline best practices for cybersecurity.
42. NIST Cybersecurity Framework: A framework that outlines best practices for cybersecurity.
43. ISO 27001: An international standard for information security management.
44. COBIT: A framework for IT governance and management.
45. PCI-DSS: A standard for payment card industry security.
46. HIPAA: A standard for healthcare industry security.
47. GDPR: A regulation for protecting personal data in the EU.
48. Data Encryption: Encrypting data to protect it from unauthorized access.
49. Access Control: Controlling who has access to systems and data.
50. Identity Management: Managing user identities and access.
51. Single Sign-On (SSO): Authentication systems that allow users to access multiple systems with a single set of credentials.
52. Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Authentication systems that require multiple forms of verification.
53. Password Management: Managing passwords to prevent unauthorized access.
54. Security Orchestration: Automating security incident response.
55. Threat Intelligence Platforms: Platforms that provide threat intelligence and analytics.
56. Security Monitoring: Monitoring systems and data for potential security threats.
57. Incident Response Tools: Tools that help respond to security incidents.
58. Digital Forensics Tools: Tools that help collect and analyze digital evidence.
59. Cybersecurity Training: Training programs that educate users about security best practices.
60. Security Awareness: Educating users about security best practices.
61. Phishing Protection: Protecting against phishing attacks.
62. Ransomware Protection: Protecting against ransomware attacks.
63. Malware Protection: Protecting against malware.
64. Denial of Service (DoS) Protection: Protecting against DoS attacks.
65. Web Application Security: Securing web applications.
66. Network Security Monitoring: Monitoring network traffic for potential security threats.
67. Security Information Management: Managing security-related information.
68. Event Management: Managing security-related events.
69. Incident Management: Managing security incidents.
70. Problem Management: Identifying and resolving security problems.
71. Change Management: Managing changes to systems and data.
72. Configuration Management: Managing system configurations.
73. Patch Management: Managing patches for systems and applications.
74. Vulnerability Management: Identifying and prioritizing vulnerabilities.
75. Risk Management: Managing risk to an organization’s assets.
76. Compliance Management: Managing compliance with regulatory requirements.
77. Audit Management: Managing audits and assessments.
78. Security Governance: Governing security practices and policies.
79. Security Policy Management: Managing security policies.
80. Security Standards: Establishing security standards.
81. Security Procedures: Establishing security procedures.
82. Security Guidelines: Providing security guidelines.
83. Security Awareness Training: Training users about security best practices.
84. Security Incident Response: Responding to security incidents.
85. Security Incident Management: Managing security incidents.
86. Disaster Recovery Planning: Planning for business continuity in the event of a disaster.
87. Business Continuity Planning: Planning for business continuity in the event of a disaster.
88. Cybersecurity Consulting: Consulting services that help organizations improve their cybersecurity posture.
89. Managed Security Services: Services that provide ongoing security monitoring and management.
90. Security Testing and Assessment: Testing and assessing security controls.
91. Vulnerability Assessment and Penetration Testing: Assessing and testing vulnerabilities.
92. Compliance Monitoring and Management: Monitoring and managing compliance.
93. Security Architecture and Design: Designing secure systems and architectures.
94. Cloud Security: Securing cloud-based systems and data.
95. Endpoint Security: Securing endpoint devices.
96. Network Security: Securing networks.
97. Application Security: Securing applications.
98. Data Security: Securing data.
99. Identity and Access Management: Managing user identities and access.
100. Security Orchestration, Automation, and Response: Automating security incident response.
101. Threat Intelligence and Analytics: Analyzing threat intelligence and security data.
These are just some of the essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks that organizations should consider implementing to protect their digital assets.
Pros and Cons:
- Improved security posture
- Reduced risk of cyber attacks
- Increased customer trust and confidence
- Improved compliance with regulatory requirements
Cons:
- High upfront costs
- Complexity of implementation
- Potential disruption to business operations
- Need for ongoing maintenance and updates
Conclusion:
Cybersecurity is a critical aspect of protecting digital assets in 2025. By implementing the 101 essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks outlined in this article, businesses and individuals can improve their security posture, reduce the risk of cyber attacks, and protect their digital assets.
This article provides a comprehensive guide to the 101 essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks for 2025. It covers the importance of cybersecurity, the potential benefits and drawbacks of implementing these tools and frameworks, and offers suggestions and professional pieces of advice for improving cybersecurity.
Suggestions
- Implement a defense-in-depth approach to cybersecurity
- Conduct regular security assessments and penetration testing
- Provide cybersecurity training and awareness programs for employees
- Stay up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity threats and trends
Professional Pieces of Advice:
- “Cybersecurity is a continuous process, not a one-time project.”
- “Investing in cybersecurity is not a luxury, it’s a necessity.”
- “Cybersecurity requires a holistic approach, including people, processes, and technology.”
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q: What are the most critical cybersecurity tools and frameworks?
A: The most critical cybersecurity tools and frameworks include firewalls, intrusion detection and prevention systems, encryption, and incident response plans.
Q: How can I improve my cybersecurity posture?
A: Improving your cybersecurity posture requires a holistic approach, including implementing the right tools and frameworks, providing cybersecurity training and awareness programs, and staying up-to-date with the latest cybersecurity threats and trends.
Q: What are the potential consequences of a cyber attack?
A: The potential consequences of a cyber attack include financial losses, reputational damage, compromised sensitive data, and regulatory penalties.
Thank you for reading! We hope this article has provided valuable insights and information on the 101 essential cybersecurity tools and frameworks for 2025.





No comments:
Post a Comment