Design Principles of Application Integration Architecture
Introduction
In the ever-evolving landscape of business and technology, digital transformation has become a key driver of innovation and growth. As organizations seek to remain competitive, they must adopt new technologies and strategies to integrate their systems, improve customer experiences, and streamline operations. Whether it's through Application Integration Architecture (AIA), embracing the challenges of museum marketing, enhancing sales strategies for financial institutions, optimizing Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems, or evaluating the use of Enterprise Service Bus (ESB), these topics highlight crucial areas of focus in the digital age. This blog explores each of these areas, discussing their importance, benefits, drawbacks, and key strategies for success.
Overviews
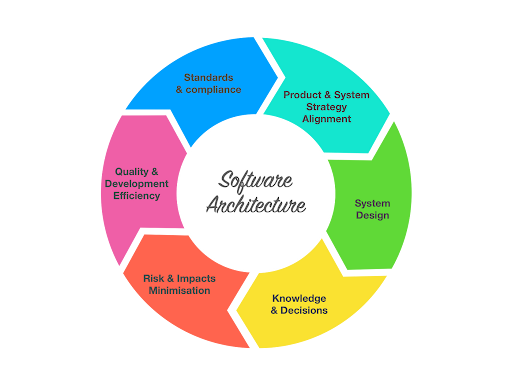
Design Principles of Application Integration Architecture: AIA is a foundational element for modern enterprises, enabling seamless communication between disparate systems. Key design principles include modularity, scalability, loose coupling, security, and data consistency.
Museum Marketing in the Digital Transformation Era: Museums face unique challenges in engaging audiences and preserving cultural heritage while adopting digital technologies. Strategies such as virtual tours, personalized experiences, and digital preservation are critical.
Strategies to Improve Sales for Financial Institutions: In the competitive financial sector, data-driven marketing, enhancing customer experience, digital transformation, and loyalty programs are vital for increasing sales and customer retention.
Improving Customer Relationship Management Systems: Optimizing CRM systems through integration, data maintenance, customization, automation, and user adoption can significantly enhance business operations and customer satisfaction.
Pros and Cons of Enterprise Service Bus in Digital Transformation: ESBs offer centralized integration, scalability, and security but come with challenges like complexity, performance overhead, and the risk of vendor lock-in.
Importance
Digital transformation is no longer optional for organizations seeking long-term success. Each of the areas discussed plays a critical role in this transformation:
Application Integration Architecture ensures that various systems within an organization can work together efficiently, facilitating better decision-making and operational effectiveness.
Museum Marketing is essential for cultural institutions to remain relevant and accessible in a digital-first world, ensuring that they continue to attract and engage diverse audiences.
Sales Strategies for Financial Institutions are crucial for maintaining a competitive edge and driving revenue growth, particularly in a market that is increasingly shifting toward digital channels.
Customer Relationship Management Systems are at the heart of effective customer engagement, helping businesses maintain strong relationships and deliver personalized experiences.
Enterprise Service Bus serves as a backbone for integrating complex systems within large organizations, supporting scalability and adaptability in digital transformation initiatives.
1. Modularity and Reusability
Modularity is about breaking down the application integration architecture into smaller, manageable components or modules. Each module should have a well-defined responsibility, making it easier to update, maintain, and reuse across different projects or contexts. Reusability reduces redundancy and speeds up the integration process by allowing developers to repurpose existing components for new applications.
2. Scalability
As organizations grow, the volume of data and the number of integrated applications will likely increase. A scalable integration architecture can handle this growth without compromising performance. Scalability should be considered from both vertical (increasing resources within the same server) and horizontal (adding more servers or nodes) perspectives.
3. Loose Coupling
Loose coupling minimizes dependencies between integrated systems, making each system more resilient to changes. By ensuring that changes in one application do not have a cascading effect on others, loose coupling enhances the flexibility and adaptability of the integration architecture.
4. Security and Compliance
Security is paramount in any architecture, particularly in an era of increasing cyber threats and stringent regulatory requirements. A robust application integration architecture must include security features such as encryption, authentication, and authorization mechanisms. Additionally, it must be compliant with relevant data protection regulations like GDPR or HIPAA.
5. Real-time Processing
In today’s fast-paced business environment, real-time data processing is often a necessity rather than a luxury. Whether it’s updating customer information across platforms or processing financial transactions, the architecture must support real-time data integration to ensure timely and accurate information flow.
6. Data Consistency and Integrity
Data consistency ensures that data remains accurate and uniform across all integrated applications. This is particularly important when multiple systems interact with the same datasets. The architecture should include mechanisms for data validation, synchronization, and conflict resolution to maintain data integrity.
7. Interoperability
Interoperability ensures that different systems, possibly built on different platforms and technologies, can work together seamlessly. This requires the use of standard communication protocols, data formats, and APIs to enable systems to exchange data and functionality without compatibility issues.
8. Monitoring and Analytics
An effective integration architecture must include robust monitoring tools to track performance, detect issues, and optimize processes. Analytics capabilities can provide insights into how the integration is functioning and where improvements can be made, enabling proactive management of the integration environment.
9. Adaptability and Future-readiness
The technology landscape is constantly evolving, and your application integration architecture must be adaptable to future changes. This includes the ability to integrate with emerging technologies like AI, IoT, and blockchain, as well as the flexibility to incorporate new business processes and requirements.
10. Cost-effectiveness
Finally, while designing an application integration architecture, it’s essential to balance functionality with cost. The architecture should not only meet the current business needs but also provide value for money by reducing operational costs, improving efficiency, and offering a significant return on investment.
Museum Marketing Challenges & Solutions in the Digital Transformation Era
The digital transformation era has revolutionized the way businesses operate, and museums are no exception. As cultural institutions, museums face unique marketing challenges in attracting and engaging audiences in an increasingly digital world. The shift towards online platforms, changing visitor expectations, and the need to preserve cultural heritage while staying relevant are some of the key hurdles. However, with the right strategies, museums can leverage digital transformation to overcome these challenges and enhance their marketing efforts.
1. Challenge: Engaging Digital Audiences
In the digital age, audiences are no longer confined to physical spaces. Engaging a global, online audience presents a significant challenge, as museums must compete with a vast array of digital content. The traditional museum experience, which relies heavily on physical interaction with exhibits, needs to be reimagined for online platforms.
2. Challenge: Adapting to Changing Visitor Expectations
Modern visitors expect personalized and engaging experiences, whether online or in-person. They seek interactive, educational, and entertaining content that goes beyond traditional static displays.
3. Challenge: Balancing Digital Innovation with Cultural Preservation
Museums have a dual responsibility to preserve cultural heritage while embracing digital innovation. Striking this balance can be challenging, especially when it comes to digitizing fragile or rare artifacts.
4. Challenge: Limited Budgets for Digital Initiatives
Many museums operate on limited budgets, making it difficult to invest in expensive digital technologies and marketing campaigns.
5. Challenge: Navigating Data Privacy Concerns
As museums collect more data on visitors through digital platforms, they must navigate complex data privacy regulations and protect visitor information.
Strategies to Improve Sales for Your Financial Institution
In a competitive financial landscape, improving sales is a top priority for financial institutions. Whether it’s increasing the uptake of loans, credit cards, or investment products, effective strategies are needed to boost sales and drive growth. Below are some key strategies that can help financial institutions enhance their sales performance.
1. Leverage Data Analytics for Targeted Marketing
Data analytics can provide valuable insights into customer behavior, preferences, and financial needs. By analyzing this data, financial institutions can segment their customer base and create targeted marketing campaigns that resonate with specific customer groups. Personalized product recommendations and tailored communication can significantly improve conversion rates.
2. Enhance the Customer Experience
A seamless and positive customer experience is crucial for driving sales. Financial institutions should focus on streamlining the customer journey, from account opening to product purchase. Offering omnichannel support, simplifying application processes, and providing excellent customer service can enhance customer satisfaction and encourage repeat business.
3. Invest in Digital Transformation
With more customers turning to online and mobile banking, investing in digital transformation is essential. Financial institutions should develop user-friendly digital platforms that make it easy for customers to explore products, apply for loans, or manage their finances. Implementing AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants can also improve customer engagement and support.
4. Cross-Sell and Upsell Products
Cross-selling and upselling are effective strategies for increasing sales. By analyzing customer data, financial institutions can identify opportunities to offer additional products that complement existing ones. For example, a customer with a savings account might be interested in a high-yield investment product or a credit card with rewards.
5. Build Stronger Customer Relationships
Building strong, long-term relationships with customers can lead to increased loyalty and higher sales. Financial institutions should focus on understanding their customers’ needs and providing personalized financial advice. Regular check-ins, financial planning sessions, and offering exclusive deals can strengthen customer relationships.
6. Optimize Sales Channels
Financial institutions should evaluate the performance of their sales channels and optimize them for better results. This includes enhancing the effectiveness of online sales channels, improving branch efficiency, and training sales staff to better understand and meet customer needs. A multichannel approach that integrates digital and physical touchpoints can help maximize sales opportunities.
7. Implement Loyalty Programs
Loyalty programs can incentivize repeat business and increase customer retention. Financial institutions can offer rewards, cashback, or discounts to customers who frequently use their products or refer new clients. A well-designed loyalty program can drive customer engagement and boost sales.
7 Tips to Improve Your Customer Relationship Management System
A robust Customer Relationship Management (CRM) system is essential for managing customer interactions, improving sales, and fostering customer loyalty. However, to fully leverage the benefits of a CRM system, it’s important to continually optimize it. Here are seven tips to improve your CRM system:
1. Integrate with Other Business Systems
Integrating your CRM system with other business systems, such as marketing automation, ERP, and customer support platforms, can provide a more comprehensive view of customer interactions. This integration ensures that data flows seamlessly across systems, enabling more informed decision-making and better customer service.
2. Clean and Maintain Your Data
Data quality is critical to the effectiveness of a CRM system. Regularly clean and update your CRM data to remove duplicates, correct errors, and ensure accuracy. Implementing data validation rules and automated data cleansing tools can help maintain data integrity.
3. Customize Your CRM
Every business has unique processes and needs, so it’s important to customize your CRM system to align with your specific requirements. This could include creating custom fields, workflows, and reports that reflect your business processes. Customization can make your CRM more user-friendly and relevant to your team.
4. Train Your Team
A CRM system is only as effective as the people using it. Provide ongoing training for your team to ensure they understand how to use the CRM effectively. Training should cover both basic functions and advanced features, helping users to maximize the system’s potential.
5. Automate Routine Tasks
Automation can significantly enhance the efficiency of your CRM system. Identify routine tasks, such as data entry, follow-up emails, or lead scoring, and automate them using CRM workflows or AI-powered tools. Automation frees up time for your team to focus on more strategic activities.
6. Monitor CRM Performance
Regularly monitor your CRM system’s performance to identify areas for improvement. This includes tracking key metrics such as user adoption rates, customer satisfaction scores, and sales pipeline health. Use this data to make informed decisions about system enhancements and process changes.
7. Foster User Adoption
User adoption is critical to the success of a CRM system. Encourage your team to actively use the CRM by highlighting its benefits, providing adequate training, and offering support. Involve users in the customization process to ensure the CRM meets their needs and is seen as a valuable tool.
Pros and Cons of Enterprise Service Bus in Digital Transformation in 2024
As organizations undergo digital transformation, the need for efficient and scalable integration solutions becomes more pressing. An Enterprise Service Bus (ESB) is one such solution that facilitates communication between different applications and services within an enterprise. However, like any technology, ESBs come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a look at the pros and cons of using an ESB in digital transformation efforts in 2024.
Pros:
1. Centralized Integration Platform
An ESB provides a centralized platform for integrating various applications and services within an enterprise. This centralization simplifies the management of integrations, reduces redundancy, and ensures consistency across different systems.
2. Scalability and Flexibility
ESBs are designed to handle complex, large-scale integrations, making them highly scalable. They support various communication protocols and data formats, offering flexibility in connecting diverse applications. As enterprises grow and evolve, an ESB can scale to accommodate new integrations without requiring significant changes to the existing infrastructure.
3. Improved Process Automation
By integrating applications through an ESB, organizations can automate business processes that span multiple systems. This automation reduces manual intervention, minimizes errors, and accelerates process execution, contributing to overall efficiency.
4. Enhanced Security
ESBs come with built-in security features, such as encryption, authentication, and authorization mechanisms, to protect data as it moves between applications. This enhances the security of data exchanges, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements and reducing the risk of data breaches.
5. Support for Legacy Systems
Many enterprises still rely on legacy systems that are critical to their operations. An ESB can facilitate the integration of these legacy systems with modern applications, enabling organizations to leverage their existing investments while embracing digital transformation.
Cons:
1. Complexity
Implementing and managing an ESB can be complex, particularly for organizations with limited technical expertise. The setup requires careful planning and ongoing management can be resource-intensive. This complexity can lead to higher implementation costs and longer deployment times.
2. Performance Overhead
ESBs introduce an additional layer of processing between integrated systems, which can result in performance overhead. In high-transaction environments, this overhead can affect the speed and responsiveness of integrations, potentially impacting business operations.
3. Vendor Lock-in
Many ESB solutions are proprietary, leading to the risk of vendor lock-in. Organizations may find it challenging to switch vendors or migrate to a different integration solution without significant effort and cost.
4. Maintenance and Upkeep
ESBs require regular maintenance to ensure they operate smoothly and securely. This includes applying updates, managing configurations, and monitoring performance. The need for ongoing maintenance can strain IT resources, especially in smaller organizations.
5. Alternatives to ESB
With the rise of microservices architecture and API-driven integrations, some organizations are moving away from traditional ESBs. These modern approaches offer greater agility and can be easier to manage, making them attractive alternatives to ESBs in certain scenarios.
In conclusion, while ESBs offer significant benefits in terms of centralized integration, scalability, and security, they also come with challenges such as complexity and performance overhead. Organizations considering an ESB as part of their digital transformation strategy in 2024 should carefully weigh these pros and cons against their specific needs and resources.
Pros
Application Integration Architecture enables seamless communication, improved data consistency, and greater business agility.
Museum Marketing in the digital era allows museums to reach global audiences, offer innovative experiences, and preserve cultural heritage in new ways.
Sales Strategies for Financial Institutions can lead to more personalized services, higher customer satisfaction, and increased sales through data-driven approaches.
Improved CRM Systems enhance customer engagement, streamline operations, and provide valuable insights for decision-making.
Enterprise Service Bus offers centralized integration, support for legacy systems, enhanced security, and scalability in complex enterprise environments.
Cons
Application Integration Architecture can be costly and complex to implement, requiring significant investment in technology and expertise.
Museum Marketing challenges include budget constraints, data privacy concerns, and the difficulty of balancing digital innovation with cultural preservation.
Sales Strategies for Financial Institutions may require significant investment in technology and training, and there’s a risk of alienating less tech-savvy customers.
CRM System Improvements may face resistance from users, require ongoing data maintenance, and need continuous investment in customization and training.
Enterprise Service Bus can introduce performance overhead, complexity, and the risk of vendor lock-in, making it less attractive in some scenarios.
Summary
Digital transformation is reshaping industries across the globe, necessitating a strategic approach to integration, marketing, sales, and customer management. Application Integration Architecture provides the foundation for seamless operations, while digital marketing strategies are essential for cultural institutions like museums. Financial institutions must adopt innovative sales strategies to stay competitive, and businesses need to continually improve their CRM systems to foster strong customer relationships. While the Enterprise Service Bus offers significant benefits for complex integrations, it’s important to weigh these against potential drawbacks such as complexity and performance issues.
Conclusion
As we move further into the digital age, organizations must embrace the opportunities and challenges that come with digital transformation. By focusing on strategic integration, innovative marketing, enhanced sales techniques, and optimized customer relationship management, businesses can position themselves for long-term success. Each of these areas plays a vital role in building a resilient, customer-centric organization that can thrive in a rapidly changing environment.
Thank You
Thank you for taking the time to explore these critical topics in digital transformation. We hope this blog provides valuable insights and strategies that you can apply to your own organization’s journey toward digital excellence.






No comments:
Post a Comment