101 Steps of Financial Transparency and Accountability
Introduction:
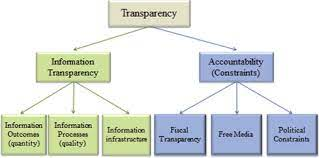
Financial transparency and accountability are essential pillars of organizational integrity and trustworthiness.
In today's complex and interconnected world, stakeholders, including investors, donors, customers,
and the public, demand greater visibility into how organizations manage their finances and make decisions.
Transparency not only fosters trust but also enables informed decision-making, enhances credibility, and strengthens relationships with stakeholders.
This comprehensive guide presents 101 steps to enhance financial transparency and accountability within organizations.
These steps encompass a wide range of strategies, from establishing clear policies and robust
accounting systems to engage with stakeholders and promote sustainability.
By implementing these measures, organizations can demonstrate their commitment to ethical conduct,
responsible stewardship of resources, and alignment with societal values and expectations.
Certainly! Here are 101 steps to enhance financial transparency and accountability within an organization:
1. Establish a clear financial reporting policy outlining the organization's commitment to transparency and accountability.
2. Develop standardized financial reporting formats and templates for consistency and clarity.
3. Implement robust accounting systems and software to accurately record and track financial transactions.
4. Assign specific roles and responsibilities for financial management, reporting, and oversight.
5. Conduct regular training sessions for staff members involved in financial management to ensure an understanding of transparency and accountability principles.
6. Publish financial reports, including balance sheets, income statements, and cash flow statements, regularly, such as quarterly or annually.
7. Provide explanations and analysis alongside financial reports to help stakeholders interpret the information effectively.
8. Utilize digital platforms and technologies to make financial information easily accessible to stakeholders, such as through online portals or dashboards.
9. Ensure financial reports are available in multiple languages to reach a diverse audience.
10. Establish a designated point of contact for inquiries related to financial information and transparency.
11. Encourage feedback from stakeholders on financial reporting practices and make adjustments as needed.
12. Conduct regular audits by independent auditors to verify the accuracy and reliability of financial information.
13. Share audit findings and recommendations with stakeholders to demonstrate accountability and transparency in addressing areas for improvement.
14. Develop a code of conduct or ethics policy outlining expected behavior related to financial matters, including conflicts of interest and fraud prevention.
15. Provide whistleblower protections and mechanisms for confidentially reporting financial misconduct or irregularities.
16. Establish an internal control framework to prevent unauthorized transactions and ensure compliance with financial policies and regulations.
17. Document financial processes and procedures in an accessible and understandable format for reference by staff members.
18. Conduct regular internal reviews and assessments of financial controls and processes to identify weaknesses or gaps.
19. Implement segregation of duties to prevent one individual from having control over all aspects of a financial transaction.
20. Require dual authorization or approval for significant financial transactions or expenditures.
21. Monitor financial performance against budgeted targets and provide explanations for variances.
22. Conduct financial forecasting and scenario analysis to anticipate potential risks and opportunities.
23. Disclose related party transactions and potential conflicts of interest to stakeholders.
24. Obtain external validation or certification of financial transparency and accountability practices from reputable organizations or industry bodies.
25. Establish an internal audit function to provide ongoing monitoring and assurance of financial management practices.
26. Develop a risk management framework to identify, assess, and mitigate financial risks effectively.
27. Ensure compliance with applicable financial regulations, laws, and reporting requirements.
28. Provide training on compliance obligations and regulatory requirements to staff members responsible for financial management.
29. Conduct regular compliance reviews and assessments to identify areas of non-compliance and take corrective action.
30. Publish an annual report summarizing financial performance, accomplishments, and challenges faced by the organization.
31. Include stakeholder testimonials or case studies in annual reports to demonstrate the impact of financial transparency and accountability on the community.
32. Seek independent verification or assurance of financial reports and disclosures to enhance credibility.
33. Engage with external stakeholders, such as investors, donors, and regulators, to solicit feedback on financial reporting practices.
34. Provide opportunities for stakeholders to participate in the financial decision-making process, such as through advisory committees or forums.
35. Establish a process for handling complaints or grievances related to financial matters and ensure timely resolution.
36. Develop key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the effectiveness of financial transparency and accountability efforts.
37. Monitor and report on progress towards achieving KPIs related to financial transparency and accountability.
38. Benchmark financial transparency and accountability practices against industry peers and best practices.
39. Participate in transparency and accountability initiatives or programs led by industry associations, non-profit organizations, or government agencies.
40. Engage with media outlets to increase public awareness of the organization's commitment to financial transparency and accountability.
41. Disclose executive compensation and board remuneration details in financial reports or annual filings.
42. Provide training on financial literacy and budget management to stakeholders, such as community members or program beneficiaries.
43. Establish a process for receiving and responding to feedback from stakeholders on financial transparency and accountability practices.
44. Develop a communication plan to disseminate financial information to stakeholders through multiple channels, such as newsletters, social media, and community meetings.
45. Host public forums or town hall meetings to discuss financial performance, priorities, and challenges with stakeholders.
46. Incorporate stakeholder input into financial planning and decision-making processes to ensure alignment with community needs and priorities.
47. Establish mechanisms for soliciting input from marginalized or underrepresented groups in financial decision-making processes.
48. Provide training on financial management and entrepreneurship to community members to empower them economically.
49. Offer financial counseling or coaching services to individuals or families experiencing financial difficulties.
50. Collaborate with local financial institutions to promote access to affordable banking and financial services in underserved communities.
51. Advocate for policies and initiatives that promote financial inclusion, such as microfinance programs or credit unions.
52. Support community-led initiatives aimed at addressing systemic barriers to financial inclusion and economic empowerment.
53. Facilitate partnerships with government agencies, non-profit organizations, and private sector entities to leverage resources and expertise in support of financial transparency and accountability efforts.
54. Allocate funding or resources to support capacity-building initiatives for community-based organizations working on financial literacy and empowerment.
55. Provide scholarships or grants to support education and skill development programs for individuals from disadvantaged backgrounds.
56. Offer incentives or rewards for individuals or organizations that demonstrate exemplary practices in financial transparency and accountability.
57. Engage with youth organizations or schools to integrate financial literacy education into curriculum or extracurricular activities.
58. Develop online resources and tools to enhance access to financial education and information for individuals with limited mobility or resources.
59. Advocate for policies and initiatives that promote gender equity and women's economic empowerment, such as equal pay laws or support for women-owned businesses.
60. Create mentorship or networking opportunities for women entrepreneurs to access support, guidance, and resources for business growth.
61. Offer financial incentives or grants to women-owned businesses or enterprises focused on advancing gender equality and social justice.
62. Support initiatives that provide access to affordable childcare, parental leave, and work-life balance policies to support women's participation in the workforce.
63. Establish partnerships with organizations that support women's economic empowerment and financial inclusion initiatives.
64. Advocate for policies and initiatives that promote environmental sustainability and responsible resource management.
65. Integrate environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations into financial decision-making processes and investment strategies.
66. Allocate funding or resources to support environmental conservation projects, renewable energy initiatives, or sustainable development programs.
67. Disclose environmental impact assessments and sustainability reports alongside financial reports to provide a comprehensive view of organizational performance.
68. Engage with stakeholders, such as environmental advocacy groups or local communities, to solicit input on environmental priorities and concerns.
69. Participate in voluntary environmental certification programs or standards, such as LEED certification or the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI), to demonstrate commitment to sustainability.
70. Incorporate sustainability criteria into procurement policies and supplier selection processes to promote responsible sourcing and supply chain management.
71. Establish goals and targets for reducing greenhouse gas emissions, energy consumption, and waste generation, and track progress towards achieving them.
72. Invest in renewable energy technologies, energy-efficient infrastructure, and green building initiatives to minimize environmental impact and promote resource efficiency.
73. Implement water conservation measures, such as rainwater harvesting or water-efficient landscaping, to reduce water consumption and protect local water resources.
74. Educate staff members and stakeholders on sustainable practices, such as recycling, composting, and energy conservation, to promote behavior change and collective action.
75. Engage with policymakers, industry associations, and advocacy groups to advocate for policies and regulations that promote environmental sustainability and corporate responsibility.
76. Participate in collaborative initiatives or partnerships focused on addressing global environmental challenges, such as climate change mitigation or biodiversity conservation.
77. Support community-based conservation projects, habitat restoration efforts, or environmental education programs to raise awareness and promote stewardship of natural resources.
78. Integrate sustainability principles into corporate governance structures, board oversight processes, and executive compensation frameworks to align incentives with long-term environmental goals.
79. Disclose information on environmental risks, liabilities, and performance metrics in financial reports and disclosures to provide transparency to investors and stakeholders.
80. Conduct regular environmental audits and assessments to evaluate compliance with environmental regulations, identify areas for improvement, and implement corrective actions.
81. Engage with investors, shareholders, and financial analysts to communicate the organization's environmental performance and sustainability initiatives effectively.
82. Participate in industry benchmarking exercises, sustainability indices, or disclosure frameworks to compare environmental performance with peers and demonstrate leadership in sustainability.
83. Establish partnerships with academic institutions, research organizations, and think tanks to support research and innovation in sustainable finance and environmental management.
84. Engage with local communities, indigenous peoples, and other stakeholders affected by environmental activities to address concerns, respect rights, and ensure equitable outcomes.
85. Collaborate with supply chain partners, vendors, and contractors to promote sustainability practices throughout the value chain and encourage the adoption of responsible business practices.
86. Provide training and capacity-building support to suppliers and contractors on environmental management, compliance requirements, and sustainable sourcing practices.
87. Require suppliers and contractors to adhere to sustainability standards, codes of conduct, or certification schemes as a condition of doing business with the organization.
88. Establish monitoring and verification mechanisms to assess supplier compliance with environmental requirements and address non-compliance through corrective action plans.
89. Conduct supplier assessments and audits to evaluate environmental performance, identify risks, and prioritize engagement and improvement efforts.
90. Collaborate with industry associations, multi-stakeholder initiatives, and supply chain platforms to share best practices, resources, and tools for promoting sustainable sourcing.
91. Provide incentives or recognition for suppliers and contractors that demonstrate leadership in sustainability and environmental performance.
92. Incorporate sustainability criteria into procurement decisions, contract terms, and supplier evaluation processes to incentivize sustainable practices and drive positive change.
93. Establish goals and targets for increasing the proportion of sustainably sourced materials, products, and services in procurement operations, and track progress towards achieving them.
94. Implement supplier development programs to support capacity-building, innovation, and investment in sustainability initiatives among suppliers and contractors.
95. Engage with stakeholders, such as customers, investors, and NGOs, to solicit feedback on sustainability priorities and expectations for responsible sourcing practices.
96. Provide transparency and disclosure on procurement practices, supplier relationships, and sustainability performance to build trust and accountability with stakeholders.
97. Conduct risk assessments and due diligence processes to identify and address environmental, social, and governance (ESG) risks within the supply chain.
98. Collaborate with suppliers and contractors to implement improvement plans, corrective actions, and continuous improvement initiatives to address identified ESG risks and opportunities.
99. Monitor and evaluate supplier performance on sustainability metrics, such as carbon emissions, water usage, and labor standards, and provide feedback for improvement.
100. Integrate sustainability criteria into supplier selection, evaluation, and performance management processes to ensure alignment with organizational values and goals.
101. Communicate the organization's commitment to responsible sourcing, ethical procurement, and sustainability to stakeholders through public statements, reports, and communications channels.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, financial transparency and accountability are critical elements of organizational governance and sustainability.
By adopting the 101 steps outlined in this guide, organizations can foster a culture of openness, integrity, and trust that benefits all stakeholders.
From disclosing financial information to engaging with stakeholders and promoting sustainability,
these steps provide a roadmap for organizations to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape while upholding the highest standards of transparency and accountability.
Ultimately, by prioritizing transparency and accountability, organizations can build stronger relationships with stakeholders, mitigate risks, and drive long-term success and impact.
These steps can serve as a guide for organizations seeking to enhance financial transparency and accountability, improve sustainability practices,
and promote responsible sourcing throughout their operations and supply chains.
By prioritizing transparency, accountability, and sustainability, organizations can build trust with stakeholders, mitigate risks, and create long-term value for society and the environment.
Thank you








No comments:
Post a Comment