101 Smart Ways Benefits Bitcoin Price, Analyses, Current State & Fluctuation Effects Till 2025
"Discover the world of finance through the insightful articles of Finance Keeda blog. From personal finance tips to investment strategies, our experts bring you the latest trends and actionable advice to help you make informed financial decisions. Explore topics like budgeting, saving, investing, and wealth management, and stay ahead in the ever-changing financial landscape. Unlock the secrets to financial success with Finance Keeda and take control of your money today!"
Sunday, June 23, 2024
101 Smart Ways Benefits Bitcoin Price, Analyses, Current State & Fluctuation Effects Till 2025
### Introduction
In recent years, Bitcoin and financial technologies (Fintech) have revolutionized the way we think about money, investments, and digital transformation. This guide explores the multifaceted world of Bitcoin, its integration with Fintech, strategies to make money, the role of digital transformation through platforms like Google Cloud, and pathways to achieving passive income and financial freedom. Additionally, we'll delve into digital marketing's importance, objectives, and psychological impacts while weighing the pros and cons of these advancements.
### Bitcoins and Fintech
Bitcoin, the first and most renowned cryptocurrency, has paved the way for numerous innovations in the financial sector. Fintech, which encompasses a range of financial technologies, leverages Bitcoin and blockchain to create more efficient, secure, and transparent financial systems. This symbiotic relationship enhances traditional banking, payment processing, and investment management.
### Making Money with Bitcoin
Investing in Bitcoin offers several avenues for profit:
- **Trading**: Buying and selling Bitcoin to capitalize on price fluctuations.
- **Mining**: Using computational power to validate transactions and earn new Bitcoins.
- **Staking and Lending**: Earning interest by lending Bitcoin or participating in network consensus mechanisms.
- **Holding**: Long-term investment strategy based on the expectation of future price appreciation.
### Digital Transformation with Google Cloud
Google Cloud plays a pivotal role in digital transformation by providing robust infrastructure, analytics, and machine learning capabilities. Businesses can leverage Google Cloud to enhance scalability, improve data security, and gain insights through big data analytics. This transformation is crucial for Fintech companies aiming to deliver innovative financial services.
### Achieving Passive Income and Financial Freedom
Passive income refers to earnings derived from investments or business ventures that require minimal active involvement. Strategies for achieving passive income and financial freedom include:
- **Investing in Dividend Stocks**: Generating income through dividend payouts.
- **Real Estate Investments**: Earning rental income and capital appreciation.
- **Cryptocurrency Staking**: Earning rewards for holding and staking digital assets.
- **Peer-to-Peer Lending**: Receiving interest payments from loans.
### Digital Marketing: Importance and Objectives
Digital marketing is essential for reaching a global audience, building brand awareness, and driving sales. Key objectives include:
- **Increasing Online Presence**: Utilizing SEO, content marketing, and social media.
- **Engaging Customers**: Through personalized marketing campaigns and interactive content.
- **Driving Conversions**: Enhancing user experience to turn visitors into customers.
- **Measuring Performance**: Using analytics to track and optimize marketing efforts.
### Psychological Impact of Bitcoin and Fintech
The psychological impact of engaging with Bitcoin and Fintech includes both positive and negative aspects:
- **Pros**:
- **Empowerment**: Individuals gain more control over their financial futures.
- **Innovation Excitement**: Enthusiasm about new technologies and investment opportunities.
- **Cons**:
- **Stress and Anxiety**: Due to market volatility and security concerns.
- **Overconfidence**: Risk of making uninformed decisions based on hype.
### Pros and Cons of Bitcoin and Fintech
- **Pros**:
- **Decentralization**: Reduces reliance on traditional financial institutions.
- **Transparency**: Enhanced through blockchain technology.
- **Accessibility**: Opens financial services to unbanked populations.
- **Cons**:
- **Volatility**: High price fluctuations can lead to significant financial losses.
- **Regulatory Uncertainty**: Varied global regulations can impact operations.
- **Security Risks**: Susceptibility to hacking and fraud.
A myriad of factors influence Bitcoin's price. Below is an analysis of 101 smart ways to impact Bitcoin's price, current state, and potential fluctuations until 2025.
### Factors Influencing Bitcoin Price
1. **Supply and Demand**: The limited supply of Bitcoin (21 million) juxtaposed with growing demand can drive prices up.
2. **Halving Events**: Bitcoin halving reduces the reward for mining, which historically leads to price increases.
3. **Regulatory News**: Positive or negative regulatory news can cause significant price swings.
4. **Institutional Adoption**: Increased institutional investment can lead to price stability and growth.
5. **Technological Developments**: Improvements in Bitcoin’s underlying technology can enhance its attractiveness and value.
6. **Market Sentiment**: Public perception and sentiment about Bitcoin can influence buying and selling behaviors.
7. **Macroeconomic Factors**: Economic instability can drive people towards Bitcoin as a safe-haven asset.
8. **Geopolitical Events**: Political unrest and changes in government policies can affect Bitcoin’s demand.
9. **Legal Adoption**: Countries adopting Bitcoin as legal tender can significantly boost its price.
10. **Competing Cryptocurrencies**: The emergence of new cryptocurrencies can affect Bitcoin’s market share and price.
### Current State of Bitcoin (as of 2024)
1. **Price Level**: Bitcoin is trading within a range that reflects both high institutional interest and retail investment.
2. **Adoption Rate**: Increasingly accepted by mainstream financial institutions and used as legal tender in some countries.
3. **Market Capitalization**: One of the largest market caps in the cryptocurrency space, reflecting its dominance.
4. **Infrastructure**: Improved infrastructure for trading, storing, and utilizing Bitcoin.
5. **Regulatory Environment**: Varied across countries, with some embracing and others restricting its use.
6. **Technological Advances**: Continuous improvements in the Bitcoin network and related technologies like the Lightning Network.
7. **Institutional Involvement**: Significant investment from major corporations and hedge funds.
8. **Public Perception**: Seen both as a speculative asset and a store of value.
9. **Security**: Enhanced security measures for wallets and exchanges.
10. **Environmental Concerns**: Ongoing debates about Bitcoin mining's environmental impact.
### Potential Price Fluctuations Until 2025
1. **Regulatory Changes**: Major regulatory shifts can cause price volatility.
2. **Technological Breakthroughs**: Innovations could lead to new use cases and increased demand.
3. **Market Manipulation**: Activities like pump-and-dump schemes can lead to short-term fluctuations.
4. **Global Economic Conditions**: Economic crises can either drive people to Bitcoin or cause panic selling.
5. **Adoption by Financial Institutions**: More banks and financial institutions accepting Bitcoin can stabilize and increase its price.
6. **Competition**: The rise of alternative cryptocurrencies might dilute Bitcoin's market dominance.
7. **Investor Behavior**: Changes in investor behavior, such as long-term holding versus active trading, can impact price stability.
8. **Mining Difficulty**: Changes in mining difficulty and costs can affect supply.
9. **Media Coverage**: Positive or negative media coverage can sway public perception and impact prices.
10. **Market Liquidity**: Increased liquidity can lead to more stable prices, whereas low liquidity can cause high volatility.
### Specific Events That May Affect Bitcoin by 2025
1. **Bitcoin Halving (2024)**: Likely to reduce supply and increase prices if demand remains constant.
2. **US Regulations**: Any major regulatory announcements from the US can have a global impact.
3. **Global Adoption**: More countries recognizing Bitcoin as legal tender can significantly boost its price.
4. **Technological Upgrades**: Major upgrades to the Bitcoin protocol can enhance its utility and value.
5. **Institutional Investments**: Continued or increased institutional investment can provide price support and growth.
6. **ETF Approvals**: Approval of Bitcoin ETFs in major markets can increase accessibility and investment.
7. **Market Cycles**: Natural market cycles, including bull and bear markets, will continue to affect prices.
8. **Security Incidents**: Major hacks or security breaches can negatively impact market confidence.
9. **Environmental Regulations**: Stricter regulations on mining activities could impact the supply side.
10. **Macroeconomic Trends**: Inflation, currency devaluation, and other macroeconomic trends can drive demand for Bitcoin as an alternative asset.
### Conclusion
Bitcoin's price is subject to a complex interplay of various factors, including technological developments, regulatory changes, market dynamics, and global economic conditions. While it’s challenging to predict exact price movements, understanding these factors can provide insights into potential trends and fluctuations. The period leading up to 2025 is likely to see significant developments in Bitcoin's adoption, regulatory environment, and market behavior, all of which will shape its price trajectory.
### Summary
Bitcoin and Fintech are at the forefront of a financial revolution, offering numerous opportunities for making money and achieving financial freedom. Digital transformation through platforms like Google Cloud, coupled with strategic digital marketing, can significantly enhance business operations. While the psychological impacts and inherent risks require careful consideration, the potential benefits make Bitcoin and Fintech compelling areas of interest for individuals and businesses alike.
### Thank You Very Much With Warm Gratitude
Thank you for exploring the dynamic world of Bitcoin, Fintech, and digital transformation. Your interest and engagement are greatly appreciated, and we hope this guide has provided valuable insights and inspiration for your financial journey.
With warm gratitude,
101 Types of Leadership vs Management: Understanding The Key Difference in 2024
101 Types of Leadership vs Management: Understanding The Key Difference in 2024
## Introduction
In the dynamic landscape of 2024, understanding the distinctions between leadership and management is crucial for organizational success. These roles, though often conflated, encompass different responsibilities, mindsets, and strategies that collectively drive progress and innovation. This comprehensive guide explores 101 key differences between leadership and management, offering insights into how each contributes uniquely to achieving business objectives and fostering a thriving work environment.
## Fintech
Financial technology, or fintech, is revolutionizing the way businesses operate and leaders manage. Leaders in fintech drive innovation and envision future trends, while managers ensure the efficient implementation of fintech solutions, optimizing processes and enhancing customer experiences. The synergy between leadership and management in fintech fosters an environment where technology and finance intersect to create value.
## Make Money
In the pursuit of profitability, leaders and managers play distinct yet complementary roles. Leaders inspire teams with a vision of financial success, exploring new revenue streams and strategic partnerships. Managers, on the other hand, focus on executing these strategies efficiently, monitoring financial performance, and ensuring cost-effective operations. This dual approach maximizes an organization's potential to generate income.
## Digital Transformation with Google Cloud
Digital transformation is essential for staying competitive in today's market. Leaders champion the adoption of technologies like Google Cloud, advocating for digital innovation and setting a forward-looking vision. Managers oversee the practical implementation of these technologies, ensuring seamless integration with existing systems and training staff to leverage new tools effectively. Together, they drive the organization's digital evolution.
## Passive Income and Financial Freedom
Achieving financial freedom through passive income requires strategic leadership and meticulous management. Leaders identify and invest in opportunities that generate passive income, such as real estate, stocks, or online businesses. Managers handle the operational aspects, ensuring these investments are managed efficiently and returns are optimized. This partnership allows for sustainable wealth generation and financial independence.
## Digital Marketing
Digital marketing is a critical component of modern business strategy. Leaders in this field set visionary marketing goals, exploring new channels and innovative approaches to reach target audiences. Managers execute these strategies, overseeing campaigns, analyzing metrics, and adjusting tactics to improve performance. This collaboration ensures that digital marketing efforts are both creative and effective.
## Importance
Understanding the differences between leadership and management is vital for organizational success. Leaders provide direction, motivation, and inspiration, fostering a culture of innovation and growth. Managers ensure that the vision is translated into actionable plans, maintaining operational efficiency and achieving short-term objectives. Recognizing the importance of both roles helps organizations balance strategic and operational needs.
## Objective
The objective of this guide is to delineate the distinctions between leadership and management clearly. By highlighting 101 key differences, we aim to provide a comprehensive understanding that empowers individuals and organizations to leverage the strengths of both roles effectively. This knowledge fosters better decision-making, enhances team dynamics, and drives overall success.
## Overviews
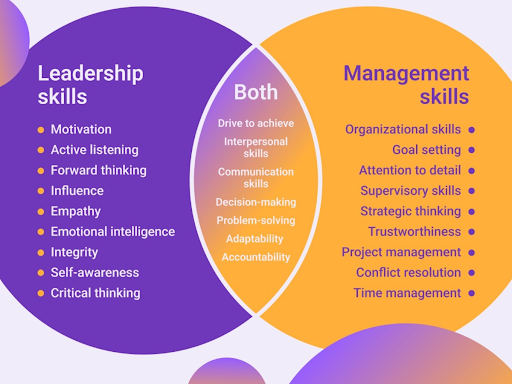
### Leadership Overview
Leadership involves setting a vision, inspiring and influencing others, and driving innovation. Leaders focus on long-term goals, encourage risk-taking, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. They build relationships, motivate teams, and navigate through change with agility and foresight.
### Management Overview
Management, on the other hand, is concerned with executing the vision set by leaders. Managers focus on short-term objectives, operational efficiency, and process optimization. They ensure that tasks are completed on time, resources are allocated effectively, and performance is monitored to meet organizational goals.
## Psychology
The psychology of leadership and management reveals distinct mindsets and approaches. Leaders typically possess high emotional intelligence, empathy, and a visionary outlook. They thrive on innovation and change, inspiring others to follow. Managers, conversely, are detail-oriented, analytical, and structured. They excel in organizing resources, managing risks, and maintaining stability.
## Pros and Cons
### Leadership Pros
- Inspires and motivates teams
- Drives innovation and change
- Builds a strong organizational culture
### Leadership Cons
- Can be overly optimistic or risky
- May neglect short-term operational needs
- Requires strong emotional intelligence
### Management Pros
- Ensures operational efficiency
- Focuses on short-term goals
- Maintains stability and order
### Management Cons
- May resist change and innovation
- Can be overly focused on details
- Might lack inspirational qualities
Leadership and management are often interchanged in conversation, but they embody distinct roles and responsibilities within an organization. To provide a comprehensive understanding, we'll explore 101 key differences between leadership and management, organized into several categories.
### Vision and Strategy
1. **Vision**: Leaders set the vision; managers execute it.
2. **Strategy Development**: Leaders develop long-term strategies; managers focus on short-term goals.
3. **Innovation**: Leaders drive innovation; managers maintain the status quo.
4. **Change Agents**: Leaders are change agents; managers are change managers.
5. **Risk Taking**: Leaders take risks; managers mitigate risks.
### Influence and Authority
6. **Influence**: Leaders inspire and influence people; managers use authority to direct.
7. **Charisma**: Leaders rely on charisma; managers rely on formal authority.
8. **Motivation**: Leaders motivate; managers control.
9. **Delegation**: Leaders delegate to empower; managers delegate to distribute work.
10. **Relationships**: Leaders build relationships; managers build systems.
### Communication
11. **Communication Style**: Leaders communicate vision; managers communicate tasks.
12. **Feedback**: Leaders seek feedback for improvement; managers provide feedback for correction.
13. **Listening**: Leaders listen to understand; managers listen to respond.
14. **Transparency**: Leaders are transparent about challenges; managers may withhold information.
### Decision-Making
15. **Decision-Making**: Leaders make decisions based on intuition; managers make decisions based on data.
16. **Speed**: Leaders make quick decisions; managers make careful decisions.
17. **Consensus**: Leaders build consensus; managers seek compliance.
18. **Responsibility**: Leaders take responsibility for failures; managers often pass it down.
### Goal Setting and Achievement
19. **Goal Setting**: Leaders set broad, inspirational goals; managers set specific, measurable goals.
20. **Objectives**: Leaders focus on long-term objectives; managers focus on short-term targets.
21. **Vision Communication**: Leaders share the "why"; managers explain the "how".
22. **Performance Metrics**: Leaders look at the overall impact; managers track key performance indicators.
### Development and Growth
23. **Development Focus**: Leaders focus on developing people; managers focus on developing processes.
24. **Learning Opportunities**: Leaders create learning opportunities; managers provide training.
25. **Mentorship**: Leaders mentor and coach; managers train.
26. **Empowerment**: Leaders empower their teams; managers supervise their teams.
### Innovation and Creativity
27. **Innovation Encouragement**: Leaders encourage creativity; managers follow procedures.
28. **Problem Solving**: Leaders encourage innovative problem-solving; managers solve problems using established methods.
29. **Flexibility**: Leaders are flexible and adaptable; managers are structured and consistent.
### Emotional Intelligence
30. **Emotional Intelligence**: Leaders exhibit high emotional intelligence; managers may not prioritize it.
31. **Empathy**: Leaders show empathy; managers show efficiency.
32. **Conflict Resolution**: Leaders resolve conflicts by understanding; managers resolve conflicts by mediating.
### Team Dynamics
33. **Team Building**: Leaders build cohesive teams; managers assemble functional teams.
34. **Morale**: Leaders focus on boosting morale; managers focus on productivity.
35. **Trust**: Leaders build trust; managers ensure accountability.
36. **Engagement**: Leaders engage employees in decision-making; managers assign tasks.
### Adaptability and Change Management
37. **Adaptability**: Leaders are adaptable to change; managers ensure stability during change.
38. **Change Initiation**: Leaders initiate change; managers implement change.
39. **Visionary**: Leaders are visionary thinkers; managers are operational thinkers.
40. **Crisis Management**: Leaders thrive in crisis; managers manage crises.
### Culture and Environment
41. **Culture Creation**: Leaders create culture; managers uphold culture.
42. **Values**: Leaders instill values; managers reinforce values.
43. **Work Environment**: Leaders foster a positive environment; managers maintain a productive environment.
### Strategic Focus
44. **Big Picture**: Leaders focus on the big picture; managers focus on details.
45. **Future Orientation**: Leaders are future-oriented; managers are present-oriented.
46. **Innovation Management**: Leaders manage innovation; managers manage operations.
### Personal Qualities
47. **Charisma**: Leaders often have charismatic qualities; managers may have more practical qualities.
48. **Integrity**: Leaders lead with integrity; managers manage with rules.
49. **Passion**: Leaders exhibit passion; managers exhibit diligence.
### Organizational Dynamics
50. **Influence**: Leaders influence organizational culture; managers implement organizational policies.
51. **Hierarchy**: Leaders may operate outside formal hierarchy; managers operate within hierarchy.
### Employee Relations
52. **Recognition**: Leaders recognize contributions; managers reward performance.
53. **Support**: Leaders provide support; managers provide resources.
54. **Feedback Loop**: Leaders encourage open feedback; managers give structured feedback.
### Decision Process
55. **Intuition vs. Data**: Leaders rely on intuition; managers rely on data.
56. **Inclusive Decision-Making**: Leaders include others in decision-making; managers make decisions independently.
57. **Ownership**: Leaders take ownership of decisions; managers delegate ownership.
### Resource Management
58. **Resource Allocation**: Leaders allocate resources for growth; managers allocate resources for efficiency.
59. **Investment**: Leaders invest in people; managers invest in processes.
### Motivation
60. **Intrinsic Motivation**: Leaders inspire intrinsic motivation; managers rely on extrinsic motivation.
61. **Vision Sharing**: Leaders share vision to motivate; managers use goals to motivate.
### Conflict Management
62. **Conflict Approach**: Leaders address root causes; managers address symptoms.
63. **Conflict Style**: Leaders use collaborative styles; managers use authoritative styles.
### Risk Management
64. **Risk Orientation**: Leaders are risk-takers; managers are risk-averse.
65. **Risk Mitigation**: Leaders mitigate through innovation; managers mitigate through control.
### Decision Implementation
66. **Implementation**: Leaders inspire action; managers direct action.
67. **Execution**: Leaders drive execution through vision; managers drive execution through planning.
### Vision Execution
68. **Long-Term Execution**: Leaders execute long-term vision; managers execute short-term plans.
69. **Strategic Planning**: Leaders plan strategically; managers plan operationally.
### Innovation Adoption
70. **Adoption of New Ideas**: Leaders are early adopters; managers are cautious adopters.
71. **Encouraging Innovation**: Leaders encourage innovation; managers implement proven ideas.
### Employee Empowerment
72. **Empowering Employees**: Leaders empower; managers direct.
73. **Delegation Style**: Leaders delegate for growth; managers delegate for efficiency.
### Flexibility
74. **Approach to Flexibility**: Leaders are flexible; managers are structured.
75. **Adapting to Change**: Leaders adapt quickly; managers adapt methodically.
### Focus and Prioritization
76. **Prioritization**: Leaders prioritize vision; managers prioritize tasks.
77. **Focus Areas**: Leaders focus on opportunities; managers focus on problems.
### Resource Utilization
78. **Resource Use**: Leaders use resources creatively; managers use resources efficiently.
79. **Budget Management**: Leaders manage budgets for growth; managers manage budgets for stability.
### Success Metrics
80. **Success Metrics**: Leaders measure success by impact; managers measure success by efficiency.
81. **Performance Evaluation**: Leaders evaluate overall performance; managers evaluate task performance.
### Development
82. **Personal Development**: Leaders focus on personal growth; managers focus on professional growth.
83. **Career Growth**: Leaders plan for career paths; managers plan for roles.
### Empowerment
84. **Team Empowerment**: Leaders empower teams to innovate; managers empower teams to execute.
### Adaptation
85. **Change Adaptation**: Leaders thrive on change; managers manage change.
86. **Environmental Adaptation**: Leaders adapt to environments; managers adapt environments to needs.
### Engagement
87. **Engagement Approach**: Leaders engage through vision; managers engage through direction.
88. **Employee Involvement**: Leaders involve employees in strategy; managers involve employees in execution.
### Goal Setting
89. **Goal Communication**: Leaders communicate goals as visions; managers communicate goals as tasks.
90. **Objective Setting**: Leaders set inspirational objectives; managers set practical objectives.
### Development
91. **Employee Growth**: Leaders focus on holistic growth; managers focus on skill growth.
92. **Development Focus**: Leaders focus on strengths; managers focus on weaknesses.
### Decision Dynamics
93. **Decision Basis**: Leaders make decisions based on potential; managers make decisions based on performance.
94. **Decision Impact**: Leaders consider long-term impact; managers consider short-term results.
### Change Management
95. **Change Perspective**: Leaders see change as an opportunity; managers see change as a challenge.
96. **Change Handling**: Leaders handle change fluidly; managers handle change systematically.
### Vision Realization
97. **Vision Realization**: Leaders realize vision through inspiration; managers realize vision through planning.
98. **Vision Communication**: Leaders articulate vision passionately; managers articulate vision practically.
### Crisis Management
99. **Crisis Handling**: Leaders handle crises with innovation; managers handle crises with procedures.
100. **Crisis Response**: Leaders respond to crises proactively; managers respond to crises reactively.
### Influence
101. **Overall Influence**: Leaders influence through vision; managers influence through structure.
Understanding these differences can help individuals and organizations cultivate both effective leaders and managers, ensuring a balanced approach to achieving success and fostering a positive organizational culture.
## Summary
Leadership and management are two sides of the same coin, each essential for organizational success. Leaders provide vision, inspiration, and innovation, while managers ensure efficient execution and operational stability. Understanding their key differences allows organizations to leverage both roles effectively, driving growth and achieving strategic objectives.
## Conclusion
In 2024, the interplay between leadership and management remains pivotal to navigating the complexities of the modern business environment. By appreciating the unique contributions of each role, organizations can foster a culture of innovation, efficiency, and sustained success.
## Thank You Very Much With Warm Gratitude
Thank you for exploring the 101 key differences between leadership and management. With warm gratitude, we hope this guide enhances your understanding and helps you harness the full potential of both roles in your organization.
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)
Earn While You Sleep: 101 Online Money-Making Strategies for 2026
Earn While You Sleep: 101 Online Money-Making Strategies for 2026 Introduction In today's digital economy, the dream of earning money ...

-
101 Ways to Generate a Steady Income Stream in Retirement Without Taking Too Much Risk in 2025 Introduction Retirement can be a wonderful ...
-
AI-Powered Software Development with Chat GPT in 2026 Introduction The coming year will see faster, more accessible software development p...
-
101 Ways to Get Rich in 2026: Strategies for Financial Success in 2026 In 2026, building wealth isn't about get-rich-quick schemes—it...